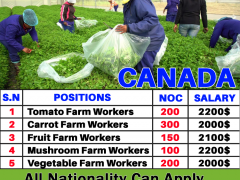
How to Apply Work to Canada from Philippines
Introduction: Overview of Working in Canada and Its Importance for Filipinos
Canada, known for its robust economy and diverse culture, has become a beacon of opportunity for people around the world, especially for Filipinos seeking better employment prospects. The allure of Canada lies not only in its potential for economic growth but also in the quality of life it offers. For many Filipinos, Canada represents a land of stability, safety, and inclusivity, making it an ideal destination for work and long-term settlement.
The importance of working in Canada for Filipinos can’t be overstated. The Philippines, while rich in culture and human resources, often faces economic challenges that drive its citizens to seek opportunities abroad. Canada’s welcoming immigration policies, coupled with a demand for skilled labor across various sectors, make it a particularly attractive destination. Filipinos, known for their hard work, adaptability, and proficiency in English, are well-positioned to contribute to and thrive in the Canadian workforce.
Moreover, the strong Filipino community already established in Canada provides a sense of belonging and support for new arrivals, easing the transition and helping them to quickly become part of their new home. This community also plays a crucial role in maintaining cultural ties, allowing Filipinos to stay connected to their heritage while embracing Canadian values.

Eligibility Criteria for Filipinos Applying to Work in Canada
When it comes to working in Canada, there are several basic requirements that all applicants, including Filipinos, must fulfill. These requirements are designed to ensure that individuals are well-suited for the Canadian labor market and can contribute positively to the country’s economy and society.
Basic Requirements
- Age: Applicants must usually be at least 18 years old. There is no upper age limit, but different rules may apply for older applicants.
- Language Proficiency: Proficiency in English or French is essential. Applicants may need to take a language test like the IELTS or TEF to prove their language skills.
- Education: A minimum level of education is often required, typically a high school diploma. However, for many skilled positions, higher educational qualifications or vocational training may be necessary.
- Work Experience: Relevant work experience in the chosen field can be a significant advantage, particularly for skilled worker categories.
- Health: Good health is a requirement, and applicants may need to undergo a medical examination.
- Criminal Record: Applicants should not have a criminal record. A police clearance certificate might be required as part of the application process.
Check This: Walk in Interview in UAE With Visa Sponsorship 2023 2024
Specific Criteria for Filipinos
In addition to these general requirements, there are specific criteria and considerations that Filipino applicants should be aware of:
- Occupation in Demand: Understanding which occupations are in demand in Canada can significantly increase the chances of approval. Sectors like healthcare, engineering, IT, and skilled trades often have a higher demand for foreign workers.
- Canadian Job Offer: Having a valid job offer from a Canadian employer can be a significant advantage. Some work permit categories require a job offer for eligibility.
- LMIA (Labour Market Impact Assessment): For many work permits, the employer needs to obtain an LMIA, which proves that no Canadian worker is available to fill the position.
- Cultural Adaptability: While not a formal requirement, demonstrating an ability to adapt to Canadian culture and work environment can be beneficial during the application process.
- Financial Stability: Applicants may need to show proof of financial means to support themselves (and their family, if applicable) upon arrival in Canada.
- Philippine-specific Procedures: Complying with the requirements set by the Philippine government for overseas workers, including securing an Overseas Employment Certificate (OEC), is also necessary.
Types of Work Permits for Filipinos in Canada
For Filipinos aiming to work in Canada, understanding the types of work permits available is crucial. Essentially, there are two primary categories of work permits: Open Work Permits and Employer-specific Work Permits. Each type has distinct features and requirements, catering to different employment situations.
Open Work Permits
- General Overview: An Open Work Permit allows the holder to work for any employer in Canada, except for those who are listed as ineligible by the government due to non-compliance with conditions or those offering services like escort services, erotic massage, or exotic dancing.
- Eligibility: This permit is typically issued under specific circumstances, such as:
- International students who have graduated from a Canadian institution.
- Spouses or common-law partners of skilled workers or international students.
- Refugees, refugee claimants, protected persons, or their family members.
- Temporary resident permit holders.
- Young workers participating in special programs like the Working Holiday program under International Experience Canada (IEC).
- Advantages: The flexibility to change employers without applying for a new work permit. This offers a significant advantage in exploring various employment opportunities.
Employer-specific Work Permits
- General Overview: Also known as a “closed” work permit, it restricts the holder to work only for the employer specified on the permit, including the location and, in some cases, the duration of work.
- Eligibility: To obtain this permit, a Filipino worker typically needs:
- A valid job offer from a Canadian employer.
- The employer to obtain a positive or neutral Labour Market Impact Assessment (LMIA) from Employment and Social Development Canada, indicating that hiring a foreign worker will not negatively affect the Canadian labor market.
- Conditions: The permit includes specific conditions such as the duration of work, the employer you can work for, the location of work, and the type of work you can do.
- Advantages: It provides a pathway for workers in skilled positions and is often a stepping stone toward permanent residency in Canada.
Finding a Job in Canada for Filipinos
For Filipinos looking to work in Canada, finding the right job is a critical step. This process involves effective job search strategies and an understanding of the industries where Filipinos are in high demand.
Job Search Strategies
- Online Job Portals: Websites like Canada’s Job Bank, Indeed Canada are excellent resources. Create a profile, upload your resume, and apply for jobs that match your skills and experience.
- Networking: Leverage social media platforms like LinkedIn to connect with industry professionals and join groups related to Canadian employment. Networking can often lead to job opportunities that are not advertised publicly.
- Recruitment Agencies: Consider registering with recruitment agencies that specialize in your field of expertise. They can help match you with suitable employers.
- Canadian Resume Format: Ensure your resume is in the Canadian format, highlighting your skills and experiences in a concise and clear manner.
- Job Fairs and Events: Participate in job fairs and career events, many of which are now held virtually, allowing international applicants to attend.
- Canadian Work Experience: If possible, gain Canadian work experience through internships or volunteer positions, which can significantly enhance your resume.
Popular Industries for Filipinos
- Healthcare: Nurses, caregivers, and medical technicians are highly sought after in Canada, given the country’s aging population and the healthcare sector’s expansion.
- Information Technology (IT): IT professionals, including software developers, network administrators, and IT project managers, are in demand due to Canada’s growing tech industry.
- Engineering: Engineers, especially in civil, mechanical, and electrical domains, are needed in various projects across Canada.
- Hospitality and Service Industry: There are opportunities for Filipinos in hospitality, food service, and retail, particularly in urban centers.
- Skilled Trades: Electricians, welders, plumbers, and carpenters are in demand in Canada’s construction and manufacturing sectors.
- Education: Educators and academic administrators are also sought after, especially those with specialization and experience.
Application Process for Work Permit in Canada for Filipinos
Navigating the application process for a Canadian work permit can be complex, but understanding it step-by-step and knowing the required documents can make it more manageable. Here’s a guide to help Filipinos through the process: How to Apply Work to Canada from Philippines
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Apply Work to Canada from Philippines
- Determine the Type of Work Permit: Decide whether you need an open work permit or an employer-specific work permit based on your job offer and circumstances.
- Obtain a Job Offer (if required): For an employer-specific work permit, secure a job offer from a Canadian employer. The employer may need to get a Labour Market Impact Assessment (LMIA) to hire you.
- Gather Necessary Documents: Before applying, ensure you have all the required documents ready (listed below).
- Complete the Application: Fill out the work permit application forms. These can be found on the Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) website. Ensure all information is accurate and complete.
- Pay the Application Fees: There are fees for processing the work permit application, which must be paid online during the application process.
- Submit the Application: You can apply online, which is faster and allows you to track the status of your application. Ensure all documents are scanned and uploaded as instructed.
- Biometrics Appointment: After applying, you might be required to give your biometrics (fingerprints and a photo). You’ll receive an instruction letter on how to proceed.
- Attend an Interview (if required): In some cases, you may be asked to attend an interview at the nearest Canadian embassy or consulate.
- Wait for the Decision: The processing time can vary based on the type of application and the specific country. You can check the status of your application online.
- Prepare for Arrival in Canada: Once approved, make travel arrangements. Remember to bring all necessary documents, including your work permit approval, for entry into Canada.
Required Documents
- Valid Passport: Your passport must be valid for the duration of your intended stay in Canada.
- Job Offer Letter (if applicable): A copy of your job offer letter or contract from the Canadian employer.
- LMIA (if applicable): A copy of the Labour Market Impact Assessment provided by your employer.
- Proof of Qualifications: Diplomas, certificates, or degrees, along with work references or experience letters.
- Language Proficiency Test Results: If required, results from an approved language test.
- Medical Exam: In some cases, a medical exam by a panel physician may be required before arrival.
- Police Clearance Certificate: To prove that you have no criminal record.
- Photographs: According to the specified format for Canadian visa applications.
- Proof of Financial Support: Evidence that you can support yourself (and your family, if applicable) in Canada.
- Completed Application Forms: The forms required for the work permit application, which can vary based on the permit type.
Role of LMIA (Labour Market Impact Assessment) in the Canadian Work Permit Process
The Labour Market Impact Assessment (LMIA) is a critical element in the Canadian work permit application process, particularly for employer-specific work permits. Understanding its role, importance, and how to obtain one is essential for Filipinos seeking employment in Canada.
Explanation and Importance
- What is an LMIA?
- The LMIA is a document that a Canadian employer may need to obtain before hiring a foreign worker.
- It is issued by Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC).
- Purpose of LMIA
- The LMIA assesses the impact that hiring a foreign worker would have on the Canadian labor market.
- It ensures that the employment of a foreign worker will not adversely affect job opportunities for Canadian citizens or permanent residents.
- Positive vs. Neutral LMIA
- A positive or neutral LMIA indicates that there is a need for a foreign worker to fill the job and that no Canadian worker is available to do the job.
- A negative LMIA means that the job should be filled by a Canadian worker.
- Importance for Employer-specific Work Permits
- For most employer-specific work permits, a positive or neutral LMIA is necessary.
- It is a part of the evidence that supports the need for a foreign worker and legitimizes their hiring in Canada.
How to Obtain an LMIA
- Employer’s Responsibility
- It is the employer’s responsibility to apply for an LMIA, not the foreign worker.
- The employer must submit an application to ESDC.
- Job Advertisement Requirement
- Before applying for an LMIA, the employer usually needs to advertise the job in Canada for at least four weeks to demonstrate efforts to hire a Canadian worker.
- Application Process
- The employer must provide various details about the position, such as job description, number of hours, and wages.
- They must also demonstrate that employing a foreign worker will positively or neutrally impact the Canadian labor market.
- Processing Time and Fees
- The processing time and fees for an LMIA can vary. Employers should check the latest information on the Government of Canada’s website.
- High-wage and low-wage positions may have different requirements and processing times.
- Providing LMIA to the Worker
- Once the LMIA is approved, the employer will receive a copy of the LMIA document.
- The employer must provide a copy of the LMIA to the foreign worker to include in their work permit application.
The LMIA is a cornerstone of Canada’s effort to ensure that the employment of foreign workers complements the Canadian labor market. For Filipinos seeking employment in Canada, having a job offer from an employer with a positive or neutral LMIA is a key step towards securing an employer-specific work permit.
Apply this: Urgent Air Canada Jobs Toronto (New Update 2023 2024) Apply Now
Financial Considerations for Filipinos Applying for Work in Canada
Financial planning is a crucial aspect of the process for Filipinos intending to work in Canada. This involves understanding both the cost of the application process and the living expenses they will encounter in Canada.
Cost of Application
- Work Permit Application Fees:
- The basic fee for processing a work permit application is typically required. As of my last update, it was CAD 155 for an individual applicant. However, fees can change, so it’s important to check the latest fee structure on the official Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) website.
- Biometrics Fee:
- Applicants might need to pay a biometrics fee, which covers the cost of collecting fingerprints and a digital photo.
- Medical Examination and Police Clearance:
- Some applicants may need to undergo a medical examination, the cost of which can vary depending on the country and the medical professional.
- A police clearance certificate, if required, also involves a fee.
- Other Possible Costs:
- Language proficiency tests, like the IELTS or TEF, which have their own associated fees.
- Professional services, if you hire an immigration consultant or lawyer.
Living Expenses in Canada
- Housing:
- Rent varies significantly depending on the city and type of accommodation. Urban areas like Toronto and Vancouver tend to be more expensive than smaller cities or rural areas.
- Utilities and Internet:
- Additional costs include utilities like electricity, heating, water, and internet, which can vary based on usage and location.
- Food and Groceries:
- The cost of food also varies. Ethnic grocery stores can be a cost-effective choice for many Filipinos.
- Transportation:
- Costs depend on the mode of transportation, with options ranging from public transit to owning a car.
- Health Insurance:
- While Canada has a public healthcare system, some provinces require new immigrants to wait a certain period before becoming eligible. Private health insurance is recommended during this period.
- Miscellaneous:
- Clothing, entertainment, and other personal expenses should also be budgeted.
Adapting to Canadian Culture for Filipinos
Moving to Canada from the Philippines involves not just a physical journey, but also a cultural transition. Understanding and adapting to Canadian culture is essential for Filipinos to integrate successfully into their new environment.
Cultural Differences
- Communication Style:
- Canadians generally value direct and clear communication but are also known for being polite and tactful. They tend to be more reserved than Filipinos in expressing emotions openly.
- Punctuality:
- Time is treated with high regard in Canada. Being on time is considered a sign of respect, unlike in the Philippines, where a more relaxed approach to time is common.
- Social Etiquette:
- Canadians value personal space and privacy. It’s common to ask permission before discussing personal matters or entering someone’s personal space.
- Workplace Culture:
- The Canadian workplace is characterized by a respect for diversity, equality, and individual rights. Hierarchies exist but are less rigid than in many Asian cultures, including the Philippines.
- Weather and Clothing:
- The Canadian climate can be a significant adjustment, with cold winters requiring appropriate clothing, which might be unfamiliar to Filipinos.
- Multiculturalism:
- Canada is highly multicultural, and there is a strong emphasis on respecting different cultures and traditions. This diversity is celebrated and protected by law.
Tips for Integration
- Learn About Canadian Culture:
- Before moving, read about Canadian customs, traditions, and social norms to get a basic understanding.
- Improve Language Skills:
- While Filipinos generally speak English, familiarizing oneself with the local accents and slangs can be helpful.
- Engage with the Community:
- Participate in local events and activities. This can be a great way to meet people and understand the Canadian way of life.
- Respect Diversity:
- Embrace the multicultural aspect of Canada and be open to meeting and learning from people of various backgrounds.
- Seek Out Filipino Communities:
- Connecting with the Filipino community in Canada can provide a sense of belonging and ease the transition.
- Be Open to New Experiences:
- Try new activities, especially those typical in Canada, like outdoor sports and barbecues in summer, or ice skating in winter.
- Adapt to the Work Environment:
- Understand and adapt to the Canadian work ethic and practices, which may differ from those in the Philippines.
- Be Patient:
- Cultural adaptation takes time. Be patient with yourself as you navigate through the initial phase of settling in a new country.
Legal Requirements and Compliance for Filipinos Working in Canada
For Filipinos working in Canada, it is crucial to understand and comply with the country’s immigration laws and be aware of the rights afforded to them as foreign workers. This knowledge not only ensures legal compliance but also helps protect their interests.
Immigration Laws
- Work Permit Validity:
- It’s essential to understand the conditions of your work permit, including its validity period, and adhere strictly to these conditions. Overstaying or working beyond the terms can lead to legal consequences and affect future immigration applications.
- Renewal and Changes in Employment:
- If you wish to extend your stay, change your job, or modify the conditions of your work, you must apply for a new work permit or an extension before your current permit expires.
- Permanent Residency (PR) Applications:
- For those seeking permanent residency, it’s important to be aware of the different pathways, like the Canadian Experience Class or Provincial Nominee Programs, and their specific requirements.
- Compliance with Canadian Laws:
- As a temporary worker, you’re expected to obey all Canadian laws, both federal and provincial. Non-compliance can result in legal action and affect your immigration status.
Rights as a Foreign Worker
- Right to Fair Wages and Working Conditions:
- Foreign workers in Canada are entitled to the same fair wages and safe working conditions as Canadian citizens and permanent residents.
- Freedom from Abuse and Exploitation:
- You have the right to work in an environment free from abuse or exploitation. This includes protection against excessive work hours, unsafe work conditions, and harassment.
- Access to Healthcare and Social Services:
- Depending on your province or territory, you may have access to healthcare services and other social benefits.
- Right to Privacy and Non-Discrimination:
- You are entitled to privacy in your personal affairs and freedom from discrimination based on race, gender, religion, or sexual orientation.
- Reporting Non-Compliance:
- If your rights are violated or you face unfair treatment, you can report to the relevant Canadian authorities without fear of retaliation affecting your immigration status.
Healthcare and Social Services for Foreign Workers in Canada
Access to healthcare and social services is a vital aspect of living and working in Canada. For foreign workers, including Filipinos, understanding how to access these services and the important information related to them is essential for a smooth and secure stay in Canada.
Access for Foreign Workers
- Eligibility for Healthcare:
- In Canada, healthcare coverage is provided by provincial and territorial governments. The eligibility for foreign workers varies by province and type of work permit.
- Generally, those with long-term work permits (usually valid for at least six months) are eligible for provincial healthcare coverage. However, there may be a waiting period (up to three months) in some provinces before coverage begins.
- Private Health Insurance:
- During any waiting period for provincial coverage, or if you are not eligible for it, private health insurance is recommended to cover medical expenses.
- Application for Health Insurance Card:
- Upon arrival in Canada and establishing residence in a province or territory, apply for a health insurance card from that province or territory.
- The application process and the time it takes to receive the card can vary.
- Coverage Details:
- Provincial healthcare typically covers necessary medical services, including visits to doctors and hospital stays. However, it may not cover prescription drugs, dental care, vision care, or medical services outside of Canada.
Important Information
- Understanding Canadian Healthcare:
- Canadian healthcare focuses on preventative care and community health. Familiarize yourself with how to access general practitioners, specialists, and emergency services.
- Social Services:
- Foreign workers may also have access to certain social services, including community health centers, mental health support, and services for families and children.
- Employment Benefits:
- Some employers offer supplementary health insurance as part of employment benefits, which can cover additional services not included in the provincial plan.
- Renewal and Validity:
- Keep track of the validity of your health insurance card and renew it as required. Ensure that your work permit is also valid to maintain eligibility for healthcare coverage.
- Emergency Services:
- In case of a medical emergency, emergency room services are available to everyone, regardless of their healthcare coverage status.
- Navigating Language Barriers:
- In areas with significant Filipino populations, there may be healthcare professionals who speak Filipino, making communication easier.
Education and Training Opportunities for Filipino Workers in Canada
Enhancing skills and knowledge is key to career advancement, especially for Filipino workers in Canada. Canada offers various education and training opportunities, helping workers upgrade their skills and integrate better into the Canadian workforce.
Upgrading Skills
- Continuing Education:
- Many educational institutions in Canada offer continuing education or adult learning programs. These courses are designed to enhance skills in specific areas, ranging from language proficiency to technical skills.
- Online Learning Platforms:
- Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning provide online courses that can be taken remotely, offering flexibility for working professionals.
- Vocational and Technical Training:
- Vocational and technical schools offer practical training in trades and skills in demand in the Canadian job market.
- Language Improvement Courses:
- Improving English or French language skills is crucial for better job opportunities. Community colleges and local community centers often offer language classes.
- Professional Certification Programs:
- Obtaining Canadian certifications or credentials in your field can enhance employability. Some professions may require Canadian certification or licensing.
Available Programs
- Government-funded Programs:
- Some provinces have government-funded programs specifically designed for immigrants, including language training and job readiness courses.
- University and College Programs:
- For more advanced training, universities and colleges offer degree and diploma programs in a wide range of fields.
- Workplace Training:
- Some employers provide on-the-job training or professional development opportunities. This could include workshops, seminars, or even funding for external courses.
- Internships and Co-op Programs:
- These programs provide practical experience and are a great way to gain Canadian work experience in your field.
- Community Organizations:
- There are numerous community organizations and non-profits that offer training programs, especially for newcomers, to help them integrate into the Canadian job market.
- Networking and Professional Associations:
- Joining professional associations related to your field can provide access to industry-specific training and networking opportunities.
Family Sponsorship and Relocation for Filipino Workers in Canada
For many Filipino workers in Canada, reuniting with their family is a priority. Understanding the process for family sponsorship and relocation, along with the challenges and potential solutions, is crucial for a smooth transition.
Process for Bringing Family
- Eligibility for Sponsorship:
- To sponsor family members to come to Canada, you must be a Canadian citizen, a permanent resident, or a temporary resident living in Canada with certain types of work permits.
- Who Can Be Sponsored:
- You can sponsor your spouse, common-law partner, dependent children, and in some cases, other relatives like parents and grandparents.
- Application Process:
- The sponsorship process involves submitting an application to Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC). This includes proving your ability to financially support your family members once they arrive.
- Financial Requirements:
- As a sponsor, you need to demonstrate that you can meet basic income requirements to support your family members. This is to ensure that they do not need to seek financial assistance from the government.
- Medical and Criminal Admissibility:
- Your family members will need to pass medical exams and criminal background checks as part of the application process.
- Processing Times:
- Processing times for family sponsorship can vary. It’s important to check current processing times and plan accordingly.
Challenges and Solutions
- Meeting Financial Requirements:
- Challenge: Proving financial stability to sponsor family members can be difficult for new workers.
- Solution: Secure stable employment and possibly seek financial advice to manage and document your finances effectively.
- Long Processing Times:
- Challenge: The processing time for family sponsorship applications can be lengthy, leading to prolonged separation.
- Solution: Plan ahead and apply as early as possible. Stay informed about the application status and use legal avenues to expedite the process, if available.
- Adjustment and Integration:
- Challenge: Family members may face challenges in adjusting to a new culture and environment.
- Solution: Access community resources, such as immigrant services and cultural associations, which can help family members acclimate to their new surroundings.
- Employment for Spouses:
- Challenge: Finding employment for spouses can be a hurdle.
- Solution: Spouses should explore job opportunities, upgrade their skills as needed, and utilize local employment resources.
- Educational Integration for Children:
- Challenge: Integrating children into the Canadian educational system.
- Solution: Research schools and educational systems in your area, and engage with local communities for support and advice.
Success Stories of Filipinos in Canada
The journey of Filipinos in Canada is often marked by resilience, hard work, and success. Their stories are not just inspirational but also provide valuable insights and learning experiences for others planning to embark on a similar path.
Inspirational Anecdotes
- From Temporary Worker to Permanent Resident:
- Many Filipinos start as temporary workers and successfully transition to permanent residency through programs like the Canadian Experience Class. Stories abound of individuals who arrived for jobs in healthcare or the service industry and, over time, established stable lives and careers for themselves and their families.
- Entrepreneurial Success:
- Some Filipinos have leveraged their skills and entrepreneurial spirit to start successful businesses in Canada. There are inspiring tales of individuals starting small – from home-based food services to tech startups – and growing their ventures into prosperous enterprises.
- Advancement in Professional Careers:
- The narratives of Filipinos climbing the corporate ladder in sectors like finance, IT, engineering, and healthcare highlight the recognition and reward of talent and hard work in the Canadian job market.
- Community Leadership:
- Many Filipinos engage actively in community services and leadership roles, contributing significantly to multiculturalism and community building in Canada. Their stories inspire a sense of duty and community involvement.
Learning from Experiences
- The Value of Resilience and Adaptability:
- These success stories often underline the importance of resilience in facing initial challenges such as cultural adjustments, climate change, and job market navigation.
- Continuous Learning and Skill Development:
- A common theme is the continual effort to learn and upgrade skills, whether it’s improving language proficiency, obtaining Canadian certifications, or pursuing higher education.
- Networking and Community Engagement:
- Building a strong network and getting involved in the Filipino and wider community in Canada has helped many in their professional and personal growth.
- Balancing Tradition and Integration:
- Successful Filipinos often find a balance between maintaining their rich cultural heritage and integrating into the Canadian way of life, enriching both their lives and those of the communities they join.
- Giving Back:
- Many successful Filipinos in Canada mentor and support new immigrants from the Philippines, creating a supportive network that fosters further success.
Challenges and Solutions for Filipinos in Canada
Filipinos moving to Canada often face a range of challenges, but with the right strategies and mindset, these obstacles can be overcome. Understanding these common issues and learning how to address them is crucial for a successful transition.
Common Issues Faced
- Cultural Adjustment:
- The shift from Philippine culture to Canadian culture can be significant, involving different social norms, communication styles, and lifestyle changes.
- Climate Adaptation:
- For many Filipinos, adapting to the Canadian climate, especially the cold winters, can be challenging.
- Employment Struggles:
- Finding employment that matches one’s skills and qualifications can be difficult, particularly due to credential recognition issues or lack of Canadian work experience.
- Language Barriers:
- Despite English proficiency, understanding local accents, slangs, and professional jargon can be a hurdle.
- Social Isolation:
- Being away from family and familiar social networks can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation.
- Financial Management:
- Managing finances, especially with the higher cost of living and unfamiliar financial systems, can be daunting.
- Navigating Healthcare and Education Systems:
- Understanding and accessing Canadian healthcare and education systems can be complex for newcomers.
How to Overcome Them
- Engage in Cultural Learning:
- Participate in cultural orientation sessions, interact with locals, and be open to new experiences to ease cultural adjustment.
- Prepare for the Climate:
- Invest in appropriate clothing and learn about living in colder climates through community resources and advice from other Filipinos in Canada.
- Credential Recognition and Upgrading Skills:
- Pursue credential recognition where necessary and consider additional training or education to meet Canadian standards.
- Language Enhancement:
- Engage in language practice sessions, join local groups, and immerse yourself in environments where you can practice and improve your language skills.
- Build a Support Network:
- Connect with Filipino communities in Canada and participate in social events and activities to build new relationships.
- Financial Planning:
- Seek financial advice, understand budgeting in the Canadian context, and learn about saving and investment options.
- Learn About Systems:
- Utilize resources provided by immigrant services to understand how the healthcare and education systems work in Canada.
Conclusion and Future Prospects for Filipinos in Canada
As we conclude, it’s evident that while the journey for Filipinos to work and settle in Canada comes with its challenges, it also offers immense opportunities for growth, stability, and success. The key points outlined in this guide provide a comprehensive roadmap for navigating the complexities of this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for Filipinos Working in Canada
- How long does it take to process a work permit for Canada from the Philippines?
- The processing time for a Canadian work permit varies depending on the type of permit and the applicant’s country. It can range from a few weeks to several months. Checking the current processing times on the Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) website is recommended for the most accurate information.
- Can I bring my family with me to Canada on a work permit?
- Yes, in many cases, you can bring your spouse/common-law partner and dependent children with you to Canada. Your spouse or partner may also be eligible to apply for an open work permit, allowing them to work in Canada.
- Are there specific industries in Canada where Filipino workers are in high demand?
- Yes, Filipinos often find opportunities in healthcare (nurses, caregivers), the service sector (hospitality, retail), skilled trades (electricians, welders), and technology (IT professionals). However, opportunities vary by region and market demand.
- What are the challenges in adapting to the Canadian work culture for a Filipino worker?
- Common challenges include navigating a new professional environment, understanding workplace etiquette in Canada, dealing with potential language barriers, and adapting to a different work-life balance and communication style.
- How can I access healthcare services in Canada as a foreign worker?
- Eligibility for healthcare services depends on your province of residence and work permit type. Generally, those with long-term work permits (usually valid for at least six months) are eligible for provincial healthcare coverage after a waiting period. Until then, or if ineligible, you should obtain private health insurance.
- Is it necessary to have Canadian work experience to find a job in Canada?
- While Canadian work experience is advantageous, it’s not always necessary. Employers also value international experience, especially if it’s relevant to the job. However, some professions may require Canadian certification or licensing.
- What are the steps for a Filipino worker to apply for permanent residency in Canada?
- The steps vary depending on the immigration program. Common pathways include the Canadian Experience Class, the Federal Skilled Worker Program, and Provincial Nominee Programs. Each has specific eligibility criteria related to work experience, language proficiency, and other factors.
More Jobs in Canada
Urgent Air Canada Jobs Toronto (New Update 2023 2024) Apply Now
Urgent Firefighter Jobs Canada (New Update 2023 2024) Apply Now